An online system for monitoring and reporting cases of adverse drug reactions and lack of efficacy of medicines comprehensively addresses the need for improved access to quality, safe, and effective medicines.
“The evaluation and analysis of PAIS system in Ukraine has brought out gaps and identified recommendations on operational PAIS system optimization and enhancing its efficacy. The implementation of new online ADRs and LOE monitoring system has become the grounds for passive PV system upgrading. The practical use of this system alongside with active PV and risk management methodologies implementation as well as the legal basis updating have laid the grounds for improving medical care and patients’ safety quality control.”
— O. Matveyeva, Head of Post-surveillance Department, State Expert Center, MOH Ukraine
The Ukraine health system has demonstrated major achievements in establishing basic systems and processes for improving the safety of medicines. However, challenges remain related to monitoring and reporting adverse drug reactions (ADRs) and lack of efficacy (LOE) and to the use of information technologies for data management and generation of signals on potential threats.
The difficulties that were historically attributed to paper-based ADR/LOE reporting systems included untimely submission of data, unreliable data quality, and the amount of information in the ADR/LOE database being insufficient for analysis. All of these impeded effective identification of potential risks and their timely mitigation.
To address the abovementioned problems, a pharmacovigilance automated information system (PAIS) was developed to ensure effective ADR/LOE monitoring and to improve reporting practices. Official use of PAIS was supported by the order of the Ministry of Health of Ukraine in August 2016.
The goal was set to create a system that automates ADR/LOE reporting and limits the need for manual operations, and this was successfully achieved by 2017.
The Piloting of PAIS
PAIS was piloted in 11 regional AIDS centers. In 2015–2016, trainings were conducted at pilot AIDS centers. Trainings were focused on the use of PAIS, and valuable feedback was collected. In total, 25 analytic specialists from the State Expert Center (SEC), 69 physicians, and 20 regional representatives of patient organizations were trained. Based on pilot results, the system was updated at the end of 2016, and in February 2017, PAIS was launched as a standard national tool for routine reporting on ADR/LOE. While the system was piloted in AIDS centers, it can be used for all medicines registered in Ukraine.
PAIS was designed and implemented as a tool that facilitates submission of ADR reports, supports data analysis, assists in causal relationship examinations, and automates the generation of signals on potential threats. The system is open to users from the public, private, and civil sectors, including medical staff, data analysts, marketing authorization holders, individual patients, and patient organizations.
“The access to PAIS and its practical implemen-tation at primary medical care level has allowed for improvement of the ADRs detection and recording, to speed up establishing of the cause and effect relationship for unfavorable clinical symptoms thus contributing to the pharmacotherapy regimen optimization and enhancing the ARV therapy efficacy and effectiveness.”
—H. Mokhniy, Deputy Chief Physician of Vinnytsia oblast AIDS center, user of PAIS
The Results
The historic paper-based reporting system was capable of showing the realistic picture. For example, in 2013 and 2014, the SEC received 660 and 632 ADR/LOE reports on paper from 82 and 78 AIDS centers, respectively. Within one year of the PAIS pilot (October 2015–September 2016), the SEC received 386 valid electronic reports from 11 AIDS centers that participated in PAIS piloting. Thus, the average number of ADR/LOE reports per facility increased more than four times.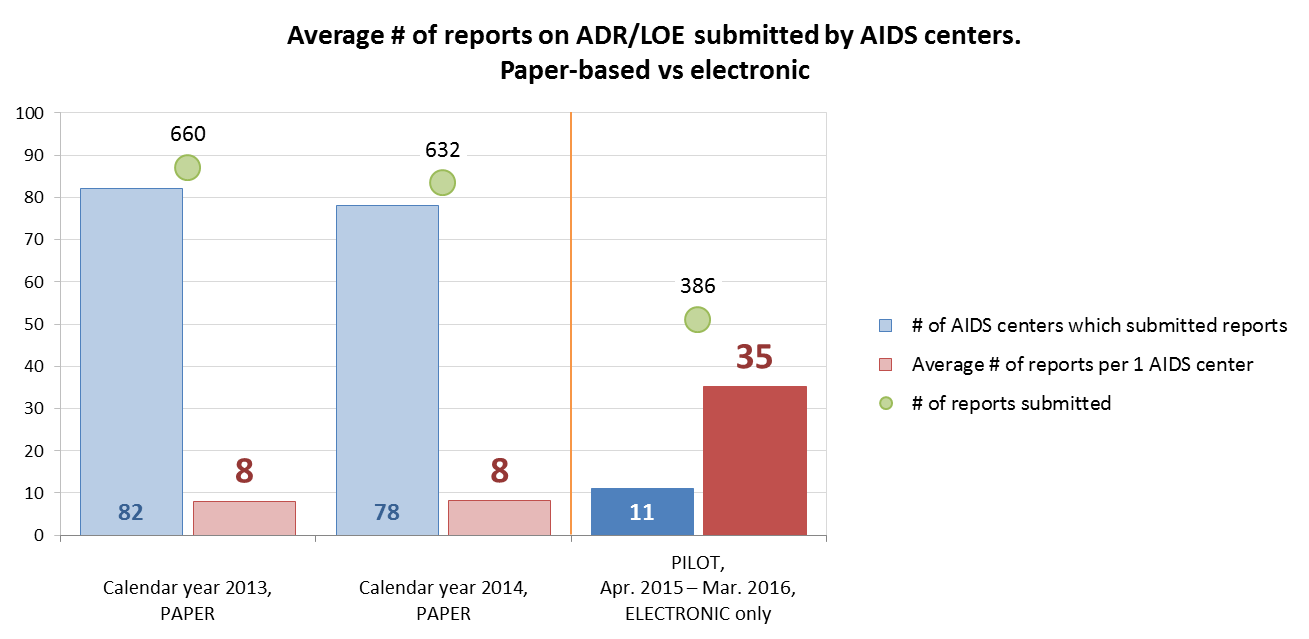
The piloting of PAIS has demonstrated the effective use of the system and the built-in analytical functions that generate standard aggregated data sheets.
Armed with these aggregated data, SEC pharmacovigilance specialists are able to analyze trends and dependencies to formulate suggestions on risks and benefits balance. These suggestions inform decision making on further utilization of medicines on the market, including confirming safety, making amendments to prescribing information, or reviewing or recalling marketing authorization.
Implementation of PAIS proved that a reduction in paperwork and the automation of routine processes significantly increases compliance of medical staff with reporting standards.
Moreover, official recognition of PAIS as the automated electronic system for ADR/LOE monitoring and reporting makes the system a sustainable IT solution that offers opportunities for all interested parties to actively contribute and positively influence access to safe, effective, and quality medicines. The next steps will be to ensure that physicians and other stakeholders beyond the pilot centers are educated on how to use the system.

